CryoSPARC on the YCRC Clusters
Install
As of February, 2026, the YCRC is transitioning to a new CryoSPARC workflow. If you would like to use this program on the clusters, please contact us.
Warning
For now (February 2026) please avoid installing CryoSPARC 5.0 or later on the clusters. It contains a breaking change to our cluster management scripts. We are working on a solution.
Warning
If you are installing a version of CryoSPARC older than 4.4.0, add the additional line
--cudapath $cuda_path \
after the --ssdpath line.
Run (2/10/2026 - Experimental)
For beta testers provided with our cryosparc-cluster-master.sh script: here is a preliminary description and walk-through on how to use it.
Please note, in contrast to our previous cryosparc workflow, the new method does not use GPU's in the batch script. Required resources for the script cryosparc-cluster-master.sh are minimal and should not be modified. The only change to the #SBATCH directives that may be needed are the running time and partition. Also note, 'worker' nodes are no longer part of this workflow.
To use the new cryosparc workflow, please use the the following steps:
-
To start your cryosparc server, submit the 'cryosparc-cluster-master.sh' script using
sbatch cryosparc-cluster-master.sh. With the script, you may (optionally) change the '#SBATCH -t -
To interact with your cryosparc server, launch a minimal OnDemand Remote Desktop session; 1 CPU, 8GB RAM on the 'devel' partition should suffice. There is no need to request more time than you expect to use your browser for, as you can always launch another Remote Desktop and get back to where you were with no information loss.
-
When submitting analysis tasks on your cryosparc server, please note that you will now have several compute lanes to choose from, including 'cpu', 'gpu' and (if you have purchased access) 'priority_cpu' and 'priority_gpu'. The cryosparc GUI will prompt you to select one of these choices once you start the job submission process by clicking 'submit job'. You must then give a job runtime (see below)
Warning
You must specify an appropriate runtime upper limit for your job, prior to clicking 'submit to lane'; otherwise, your job may be terminated prematurely. For jobs than run very quickly like micrograph imports, one hour ('1:00:00') is a safe value. However, for long jobs whose durations are uncertain, we suggest 24 hours ('24:00:00'). If you have a safe and reasonable guess that is smaller, this will help your job start sooner.
Currently this option is hidden at the bottom of the submission pane (right-hand side of the window titled 'Queue Pxxx Jxxx'). Scroll to the bottom and click on the purple box that says 'Cluster submission script variables'. The box will expand to reveal additional options, where you can click on 'Maximum runtime'.
After you click 'Submit to lane', the YCRC slurm scheduler will assign your task to an available compute node. You may then monitor your job not only through cryosparc itself, but also through the YCRC slurm tools (i.e. 'User Portal' from the OOD Utilities menu, or by the terminal command 'squeue --me').
Note
The cryosparc slurm scheduler tries to guess the amount of memory required for a job, which depends on a variety of factors. If you encounter memory-related failures, you may set the 'RAM multiplier' value under 'Cluster submission script variables' to a value greater than one.
Note
If you change your mind about job runtime after you submit to a lane, but before it starts running, you may use the following bash terminal command to adjust it, for example:
scontrol update JobId=1234567 TimeLimit=6:00:00
You may also use slurm to change the partition a job runs in (again, you need to do this before the job starts running):
scontrol update JobId=1234567 Partition=priority_gpu
Topaz support (Optional)
Topaz is a pipeline for particle picking in cryo-electron microscopy images using convolutional neural networks. It can optionally be used from inside CryoSPARC using our cluster module.
1. In an interactive cluster session, prepare an executable bash script 'topaz.sh' that loads our topaz module and runs topaz:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
if command -v conda > /dev/null 2>&1; then
conda deactivate > /dev/null 2>&1 || true # ignore any errors
conda deactivate > /dev/null 2>&1 || true # ignore any errors
fi
unset _CE_CONDA
unset CONDA_DEFAULT_ENV
unset CONDA_EXE
unset CONDA_PREFIX
unset CONDA_PROMPT_MODIFIER
unset CONDA_PYTHON_EXE
unset CONDA_SHLVL
unset PYTHONPATH
unset LD_PRELOAD
unset LD_LIBRARY_PATH
module load topaz/0.2.5-fosscuda-2020b
exec topaz $@
2. Make the topaz.sh script executable:
chmod a+x <PATH-TO>/topaz.sh
3. In a running CryoSPARC instance, add the executable '<PATH-TO/topaz.sh' to the General settings:
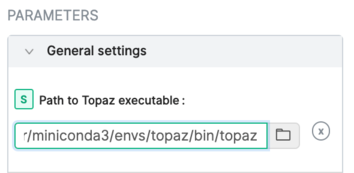
4. Consult the CryoSPARC guide
for details on using Topaz with CryoSPARC.
Troubleshoot
If you are unable to start a new CryoSPARC instance, the likeliest reason is leftover files from a previous run that was not shut down properly. Check /tmp and /tmp/${USER} for the existence of a cryosparc.sock file or a mongo.sock file. If they are owned by you, you can just remove them, and CryoSPARC should start normally. If they are not owned by you, and you have reserved the GPUs, then it is likely due to another user's interrupted job. Contact YCRC staff for assistance.
If your database won't start and you're sure there isn't another server running, you can remove lock files and try again.
# rm -f $CRYOSPARC_DB_PATH/WiredTiger.lock $CRYOSPARC_DB_PATH/mongod.lock