VNC
As an alternative to X11 Forwarding, using VNC to access the cluster is another way to run graphically intensive applications.
Open OnDemand
On the clusters, we have web dashboards set up that can run VNC for you as a job and forward your session back to you via your browser using Open OnDemand. To use the Remote Desktop tab, browse under the "interactive apps" drop-down menu item.
We strongly encourage using Open OnDemand unless you have specific requirements otherwise.
Setup vncserver on a Cluster
-
Connect to the cluster with X11 forwarding enabled. If on Linux or Mac,
ssh -Y netid@cluster, or if on Windows, follow our X11 forwarding guide. -
Start an interactive job on cluster with the
--x11flag (see Slurm for more information). For this description, we’ll assume you were given node r801u30n01:
salloc --x11
- On that node, run the VNCserver. You’ll see something like:
r801u30n01.grace$ vncserver
New 'r801u30n01.grace.ycrc.yale.edu:1 (kln26)' desktop is r801u30n01.grace.ycrc.yale.edu:1
Creating default startup script /home/kln26/.vnc/xstartup
Starting applications specified in /home/kln26/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/kln26/.vnc/r801u30n01.grace.ycrc.yale.edu:1.log
The :1 means that your DISPLAY is :1. You’ll need that later, so note it. The first time you run "vncserver", you’ll also be asked to select a password for allowing access.
On MacOS, if connecting with TurboVNC throws a security exception such as "javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException", try adding the SecurityTypes option when starting vncserver on the cluster:
vncserver -SecurityTypes VNC,OTP,UnixLogin,None
Connect from your local machine (laptop/desktop)
macOs/Linux
From a shell on your local machine, run the following ssh command:
ssh -Y -L7777:r801u30n01:5901 YourNetID@cluster_login_node
This will set up a tunnel from your local port 7777 to port 5901 on r801u30n01. You will need to customize this command to your situation. The 5901 is for display :1. In general, you should put 5900+DISPLAY. The 7777 is arbitrary; any number above 3000 will likely work. You’ll need the number you chose for the next step.
On your local machine, start the vncviewer application. Depending on your local operating system, you may need to install this. We recommend TurboVNC for Mac.
When you start the viewer, you’ll need to tell it which host and port to attach to. You want to specify the local end of the tunnel. In the above case, that would be localhost::7777. Exactly how you specify this will depend a bit on which viewer you use. E.g:
vncviewer localhost::7777
You should be prompted for the password you set when you started the server.
Now you are in a GUI environment and can run IGV or any other rich GUI application.
/home/bioinfo/software/IGV/IGV_2.2.0/igv.sh
Windows
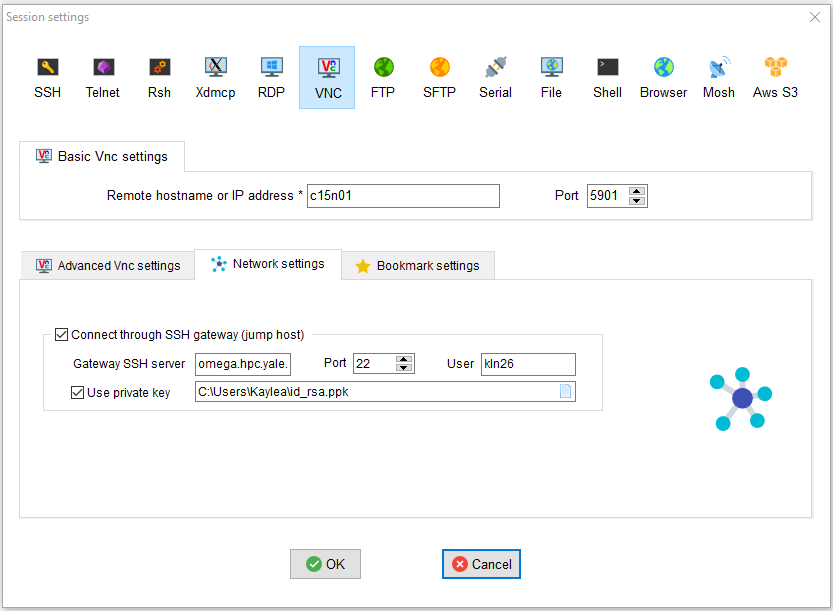
In MobaXterm, create a new Session (available in the menu bar) and then select the VNC session.
To fill out the VNC Session setup, click the "Network settings" tab and check the box for "Connect through SSH gateway (jump host). Then fill out the boxes as follows:
- Remote hostname or IP Address: name of the node running your VNC server (e.g. r801u30n01)
- Port: 5900 + the
DISPLAYnumber from above (e.g. 5901 forDISPLAY = 1) - Gateway SSH server: ssh address of the cluster (e.g. grace.ycrc.yale.edu)
- Port: 22 (should be default)
- User: netid
- Use private key: check this box and click to point to your private key file you use to connect to the cluster
When you are done, click OK. If promoted for a password for "localhost", provide the vncserver password you specified in the previous step.
If the VNC server looks very pixelated and your mouse movements seem laggy, try clicking the "Toggle scaling" button at the top of the VNC window.
Example Configuration:
Clean Up
When you are all finished, you can kill the vncserver by doing this in the same shell you used to start it (replace :1 by your display number):
vncserver -kill :1